Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
Microsite vs Landing Page: In the digital marketing world, choosing the right tools can significantly impact your campaign’s success. Microsites and landing pages are two powerful options, each with unique strengths. Knowing which one to use can help you achieve your marketing goals more effectively. This article explores the differences between microsites and landing pages, their benefits, and when to use each.
Definitions
What is a Microsite?
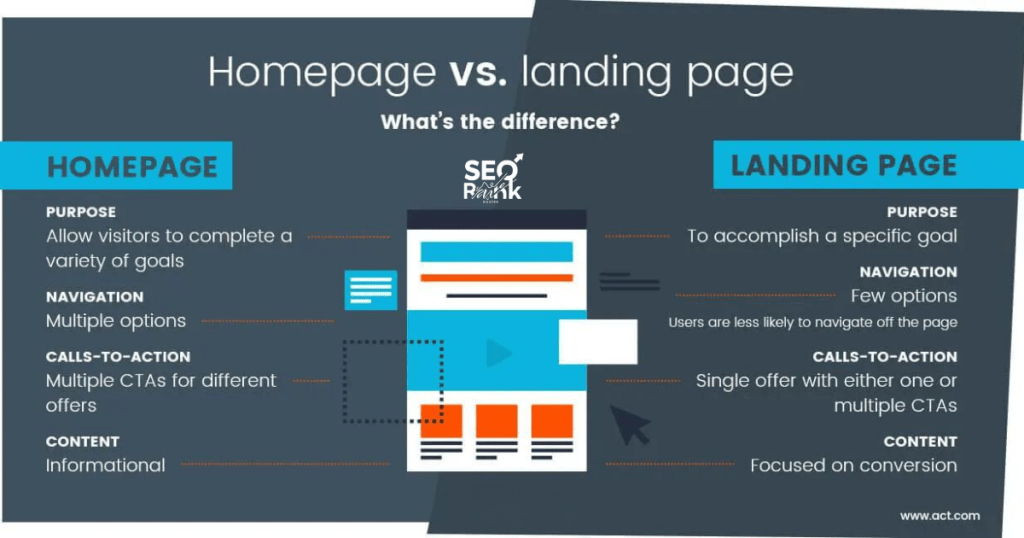
A microsite is a small, standalone website created for a specific purpose, such as a marketing campaign, product launch, or event. Unlike a landing page, a microsite can have multiple pages and its own navigation.
Characteristics of Microsites:
- Multiple pages with unique URLs
- Independent navigation
- Rich multimedia content
- Focused on specific campaigns or themes
What is a Landing Page?
A landing page is a single web page designed to achieve a specific goal, such as capturing leads or driving sales. It is where users land after clicking a link from an email, ad, or other digital source.
Characteristics of Landing Pages:
- Single page with a focused goal
- Designed for conversions (e.g., sign-ups, purchases)
- Minimal navigation to reduce distractions
- Direct and persuasive content
Purpose and Usage
Microsites: When and Why to Use Them
Microsites are perfect for detailed marketing campaigns that require extensive information and interactive elements. They are best used for:
- Product launches
- Brand storytelling
- Detailed promotional campaigns
- Event-specific content
Landing Pages: When and Why to Use Them
Landing pages excel at driving specific user actions with minimal distractions. They are ideal for:
- Lead generation
- Product promotions
- Event registrations
- Sales funnels
Structure and Design
Structure of Microsites
Microsites often include multiple pages, each focusing on different aspects of the campaign. They might feature a homepage, subpages with detailed information, and interactive sections.
Structure of Landing Pages
Landing pages are streamlined and focused. They usually consist of a headline, subheadline, brief content, and a clear call to action (CTA). Navigation is minimal to keep users focused on the goal.
Design Considerations for Microsites
- Consistent branding with the main website
- Engaging multimedia content
- Clear, intuitive navigation
Design Considerations for Landing Pages
- Minimalist design to reduce distractions
- Strong, compelling headlines and CTAs
- Easy-to-skim content layout
Content and Features
Typical Content in Microsites
Microsites often include:
- Detailed product information
- Interactive elements like quizzes or surveys
- Multimedia content such as videos and infographics
- Testimonials and case studies
Typical Content in Landing Pages
Landing pages usually feature:
- Persuasive headlines and subheadings
- Brief, impactful content
- Lead capture forms
- Clear and compelling CTAs
Key Features of Microsites
- Multiple content types and pages
- Enhanced user engagement through interactivity
- Custom domain or subdomain
Key Features of Landing Pages
- Single, focused message
- Conversion-optimized elements
- A/B testing capabilities for optimization
SEO and Marketing
SEO Strategies for Microsites
Microsites can be optimized with their own set of keywords, meta descriptions, and backlinks. They contribute to the overall SEO strategy by targeting specific long-tail keywords and providing a rich user experience.
SEO Strategies for Landing Pages
Landing pages should be optimized for specific, highly relevant keywords. Meta descriptions and title tags should be compelling and include the target keyword. Internal linking to the main website can help improve overall SEO.
Marketing Benefits of Microsites
- Enhances brand storytelling
- Increases user engagement
- Supports detailed campaigns
Marketing Benefits of Landing Pages
- High conversion rates
- Targeted marketing efforts
- Simplified user journey
Case Studies and Examples
Successful Microsite Campaigns
One notable example is Coca-Cola’s “Share a Coke” campaign, which used a microsite to let users create personalized Coke labels. This interactive experience significantly boosted engagement and sales.
Successful Landing Page Campaigns
A great example is Dropbox’s landing page for its referral program, which clearly communicated the benefits of the program and resulted in a massive increase in user sign-ups and referrals.
Pros and Cons
Pros of Using Microsites
- Versatile and rich in content
- Enhanced user engagement
- Supports complex marketing strategies
Cons of Using Microsites
- Higher development and maintenance costs
- Can dilute SEO efforts if not managed properly
Pros of Using Landing Pages
- High conversion potential
- Cost-effective and quick to deploy
- Focused and streamlined user experience
Cons of Using Landing Pages
- Limited content and scope
- May not provide enough information for complex products
Costs and Budget
Budget Considerations for Microsites
Creating a microsite can be more expensive due to the need for multiple pages, custom design, and interactive elements. However, the investment can pay off with higher engagement and conversions.
Budget Considerations for Landing Pages
Landing pages are typically less costly to create and maintain. They require fewer resources and can be quickly deployed using templates or landing page builders.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
When deciding between a microsite and a landing page, consider the campaign’s goals, complexity, and budget. Microsites are suitable for in-depth campaigns with higher budgets, while landing pages are ideal for quick, targeted conversions on a limited budget.
Performance Metrics
Measuring Success of Microsites
Key performance indicators (KPIs) for microsites include:
- Time on site
- Pages per session
- Bounce rate
- Conversion rate
- User engagement metrics
Measuring Success of Landing Pages
KPIs for landing pages focus on conversion efficiency, including:
- Conversion rate
- Bounce rate
- Click-through rate (CTR)
- Cost per acquisition (CPA)
Future Trends
Emerging Trends in Microsites
- Increased use of AI for personalized user experiences
- Enhanced interactive features and gamification
- Greater integration with social media platforms
Emerging Trends in Landing Pages
- Dynamic content personalization
- Integration with advanced analytics tools
- Use of video and rich media to boost engagement
FAQs
When would you use a microsite instead of a landing page?
Use a microsite for detailed campaigns that require multiple pages and interactive elements, such as product launches or brand storytelling.
Is it better to have a landing page or website?
It depends on your goals. A landing page is better for focused, single-goal campaigns like lead generation, while a full website is better for providing comprehensive information and multiple user interactions.
What is not recommended for a landing page?
Avoid cluttered designs, excessive navigation links, and long, unfocused content. Keep the page simple and focused on a single goal.
How many pages should a microsite be?
A microsite can range from a few pages to a dozen, depending on the campaign’s complexity and content requirements.
When should I use a landing page?
Use a landing page for specific actions like lead generation, event registrations, or product promotions where you want to drive conversions.
Is it possible to create a landing page without a website?
Yes, you can create a standalone landing page using various landing page builders and tools, even if you don’t have a full website.
Are landing pages free?
Many landing page builders offer free plans with basic features, but advanced features and custom domains usually require a paid plan.
Conclusion
Choosing between a microsite and a landing page depends on your campaign’s goals, complexity, and budget. Microsites are excellent for in-depth, interactive campaigns requiring multiple touchpoints, while landing pages excel in focused, high-conversion scenarios. Understanding their unique benefits and limitations will help you deploy the right tool for your marketing strategy, ensuring maximum impact and success.